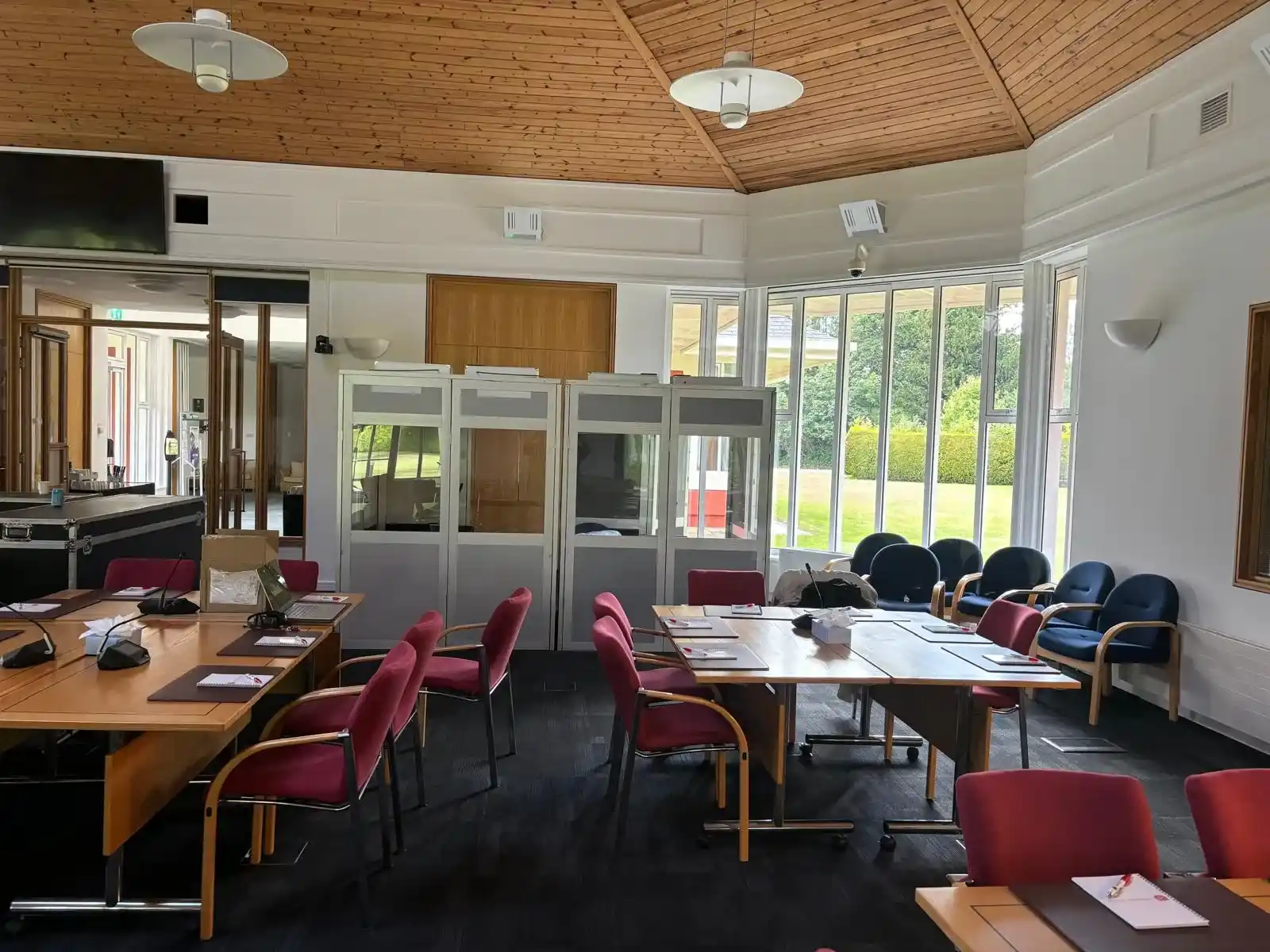
We understand that interpretation and translation are vital for bridging gaps among multiple languages. Although they both serve the same purpose, they are not the same.
So, are you confused between these two? Or which one should you choose for your next international event? If yes, then here is your brief answer. So, let’s jump in.
Definitions & Purposes Of Interpretation Vs. Translation
Interpretation
It is the art of converting everything from one language to another in real time. It’s all about facilitating the conversations and speeches. It ensures participants can communicate easily without any language barrier.
Further, there are two types of interpretations, which are:
- Simultaneous Interpretation: Interpreting the speaker’s words simultaneously while he is speaking.
- Consecutive Interpreting: Here linguist interpreter waits until the speaker finishes or pauses. For example, a multilingual event where interpreters translate a keynote speaker’s address to the audience live.
Translation
It mainly focuses on written texts. Like converting documents, books, or written content from one language to another. At the same time, they have to maintain the accuracy and meaning of the text. Further, there are three types of translation:
- Literal
- Contextual
- Creative
Translators are bound by text rules like grammar, syntax, and linguistic nuances. For example, translating a business contract from English to Arabic for a Dubai client.
Practical Differences Between Interpretation & Translation
Let’s now examine the 7 practical differences between interpretation and translation, which will help you understand them better.
1. Mode Of Delivery
Let’s be clear here: Interpretation only deals with spoken languages. On the other hand, translation strictly deals with written language, including all kinds of written materials. For example academic, business, and marketing materials.
2. Time Scale
Interpretation is a quick service. It requires interpreters to think and react quickly and respond to situations on the spot. In contrast, translation requires some time for research and precision to ensure accuracy.
3. Input Format
Interpretation can be used for live settings. The challenge is that the speaker may pause, use filler words, or even speak incomplete sentences. That makes it hard for interpreters to deal with unpolished inputs and deliver real-time solutions. Moreover, this should be done without the luxury of rewinding or rereading.
On the other hand
Translation projects involve diverse forms of input formats. For example, TV ads, scripts, manuals, podcasts, or eLearning materials. Often, these projects require specialist translators skilled in technical fields like medicine, law, and engineering.
4. Accuracy Demands
Interpreters often prioritise delivering meaning on exact wordings. That leaves out minor phrases or rephrasing to maintain conversational flow.
But
Translation allows professionals to achieve high accuracy, thanks to time research, and technology. In interpretation, perfection is harder to attain due to the fast paced of live communication.
5. Direction of Translation
Interpreters often need to work in both directions during conversations or meetings. This means they have to switch languages and translate both languages back and forth. Interpretation is a dual service that demands exceptional proficiency in both languages.
On the other hand,
Most translation projects involve converting content from one source to the target language. This job is quite simple and usually uni-directional.
6. Technology & Tools
Interpreters use audio equipment, such as microphones and headphones, in large settings and over video conferencing systems. However, interpretation is entirely manual and relies on the interpreter’s skills.
While
Translators use software tools like CAT (computer assisted translation) translator and memory to maintain consistency. Moreover, it can supported by a variety of tools:
- Translational Memory
- Terminology Management Software
- Automated Translation System
These tools can help alot to enhance security, consistency, speed, and quality.
7. Where They Can Be Use
Interpretation is mainly used in the following cases:
- International conferences
- Court Hearings
- Medical Appointments
While the translation is widely used in the following cases:
- Legal documents
- Websites and Apps
- Works of literature
8. Project Management
Interpretation usually brings minimalistic project management. Once the session concludes, the interpreter’s job is done.
But
Translation projects often require comprehensive content management systems. They require handling multiple documents, languages, and deadlines. Any part of a large project, like subtitling, demands intricate coordination and management.
9. Cost Differences
Interpretation is more expensive than translation. The main reason for its price hike is the nature of this job that demands:
- Urgency
- High skills
- And accuracy.
On the other hand, the translational cost is a bit lower and depends on the material’s complexity and length.
Which One Do You Need?
If you are about to host a live event, attend a meeting, or communicate in real time, go for interpretation. But if you’re working with documents or written material, translation is the way to go.
Hence, understanding the difference between interpretation and translation ensures you choose the right service for your needs. Both are vital for effective cross-cultural communication. They ensure your message is clear and impactful, no matter the language.